Potatoes are a staple ingredient in many households, and it’s not uncommon to find a few sprouted potatoes in the pantry. But the question remains: can you eat sprouted potatoes? The short answer is yes, but with a few caveats.
When potatoes begin to sprout, they produce glycoalkaloids, a natural toxin that can cause digestive symptoms, such as upset stomach, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In large quantities, glycoalkaloids can even lead to death.
However, the levels of glycoalkaloids in sprouted potatoes are usually low and not harmful to most people. Removing the sprouts and any green spots on the potato can reduce the risk of toxicity.

What Are Sprouted Potatoes?
Sprouted potatoes are potatoes that have started to grow shoots or sprouts from the eyes or buds on their surface. These sprouts are a sign that the potato is trying to grow into a new plant, and they can be green or white in color.
Are Sprouted Potatoes Safe to Eat?
According to Healthline, sprouted potatoes are safe to eat. However, it is important to note that the sprouts and any green parts of the potato contain a toxin called solanine, which can cause digestive problems, headaches, and in severe cases, coma and death.
What Are the Risks of Eating Sprouted Potatoes?
The risks of eating sprouted potatoes come from the solanine toxin that can be present in the sprouts and green parts of the potato. Consuming too much solanine can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause coma and death.
How Can You Tell if a Potato Is Sprouted?
You can tell if a potato is sprouted by looking for the presence of small shoots or sprouts growing from the eyes or buds on the potato’s surface. Additionally, if the potato has started to turn green, this is a sign that it has been exposed to light and may have started to sprout.

How to Properly Store Potatoes to Prevent Sprouting
To prevent potatoes from sprouting, it is important to store them in a cool, dark, and dry place. Ideally, potatoes should be stored in a location with a temperature between 45-50°F (7-10°C) and a humidity level of around 95%.
Additionally, potatoes should be stored away from other fruits and vegetables, as they can release ethylene gas that can cause potatoes to sprout more quickly.
In summary, sprouted potatoes are safe to eat as long as you remove the sprouts and any green parts of the potato. However, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with eating sprouted potatoes and to properly store potatoes to prevent sprouting in the first place.
Toxicity of Sprouted Potatoes
When potatoes start to sprout, they produce a chemical called solanine, which can be toxic to humans if ingested in large quantities. Sprouted potatoes contain higher levels of glycoalkaloids, which can also have toxic effects in humans when consumed in excess.
Glycoalkaloids are natural toxins that are produced by the potato plant as a defense mechanism against insects, fungi, and other predators.
Consuming sprouted potatoes that have high levels of glycoalkaloids can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, headaches, dizziness, and in severe cases, coma or death.
The severity of the symptoms depends on the amount of glycoalkaloids ingested and the individual’s sensitivity to them.
It is generally recommended to avoid eating sprouted potatoes, especially if they are green, wrinkled, or shriveled. These physical changes indicate that the potato has been exposed to light and has produced more solanine and glycoalkaloids.
However, if you must eat sprouted potatoes, it is best to remove the sprouts and any green-tinged parts of the potato, as these are the areas with the highest concentration of toxins.
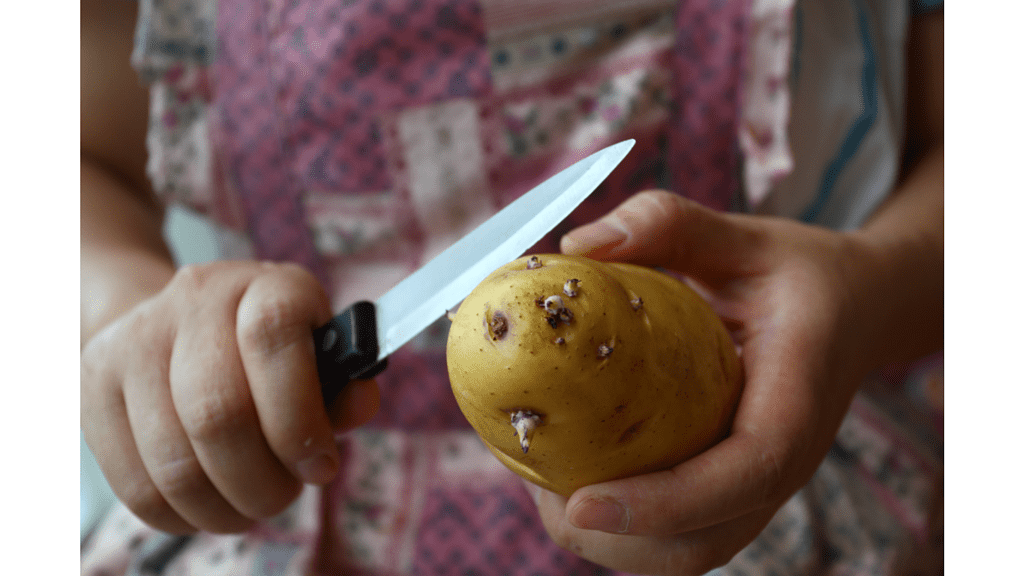

To minimize the risk of glycoalkaloid toxicity, it is also important to store potatoes in a cool, dry, and dark place, away from light and moisture.
Do not store potatoes and onions together, as the gases from onions can speed up potato sprouting.
Additionally, it is recommended to buy potatoes as you need them, rather than in bulk, to reduce the chances of sprouting and glycoalkaloid buildup.
How to Properly Store Potatoes to Prevent Sprouting
When it comes to storing potatoes, the right conditions can make all the difference in preventing sprouting. Here are some tips on how to properly store potatoes to prevent sprouting:
The Best Way to Store Potatoes
Potatoes should be kept away from heat and light, as these can cause them to sprout faster. A temperature range of 45-50°F (7-10°C) is ideal for storing potatoes. However, they can also be stored in temperatures as low as 38-42°F (3.4-5.6°C) without affecting their flavor or texture too much.
How to Store Potatoes in a Pantry
A pantry can be a good place to store potatoes as long as it is cool, dark, and dry. Potatoes can be stored in a paper bag or a cardboard box, which will help to keep them dry and prevent moisture buildup.
It’s important to check the potatoes regularly for any signs of sprouting or spoilage, and to remove any damaged or rotten potatoes immediately.

How to Store Potatoes in a Refrigerator
While storing potatoes in the refrigerator can help to prevent sprouting, it’s not the best option. The cold temperatures can cause the starches in the potatoes to convert to sugars, which can affect their flavor and texture.
If you do choose to store potatoes in the refrigerator, make sure they are in a perforated plastic bag or a paper bag to allow for air circulation.
How to Store Potatoes in a Cardboard Box
A cardboard box can be a good option for storing potatoes, as long as it is in a cool, dark, and dry place. The box should be lined with paper towels or newspaper to help absorb any excess moisture.
You should check the potatoes regularly for any signs of sprouting or spoilage, and to remove any damaged or rotten potatoes immediately.
How to Store Potatoes in a Breathable Bag
A breathable bag, such as a mesh produce bag, can be a good option for storing potatoes. The bag should be placed in a cool, dark, and dry place, and the potatoes should be checked regularly for any signs of sprouting or spoilage. Don’t forge to remove any damaged or rotten potatoes immediately to prevent them from affecting the others.
By following these tips, you can properly store potatoes to prevent sprouting and keep them fresh for longer.

Frequently Asked Questions
Are sprouted potatoes safe to eat?
According to Healthline, sprouted potatoes are still safe to eat, but the sprouts should be removed before cooking. The sprouts contain solanine, a toxic compound that can cause headaches, nausea, and digestive issues if consumed in large amounts.
What happens if you eat sprouted potatoes?
Eating sprouted potatoes with the sprouts still attached can cause digestive issues and discomfort due to the presence of solanine. However, removing the sprouts before cooking can make the potatoes safe to eat.
How long can you store potatoes before they sprout?
Potatoes can be stored for several weeks to several months depending on the storage conditions. According to Southern Living, potatoes should be stored in a cool, dry, and dark place to prevent sprouting. If stored properly, potatoes can last for up to six months.
Can sprouted potatoes be used for cooking?
Yes, sprouted potatoes can still be used for cooking, but the sprouts should be removed before cooking. The potatoes may have a slightly bitter taste due to the presence of solanine, but this can be minimized by removing the sprouts.
Is it safe to eat potatoes with eyes?
Potatoes with eyes are safe to eat, but the eyes should be removed before cooking. The eyes are the small growths on the surface of the potato and can contain solanine, which can cause digestive issues if consumed in large amounts.
What To Do with Potatoes That Sprouted
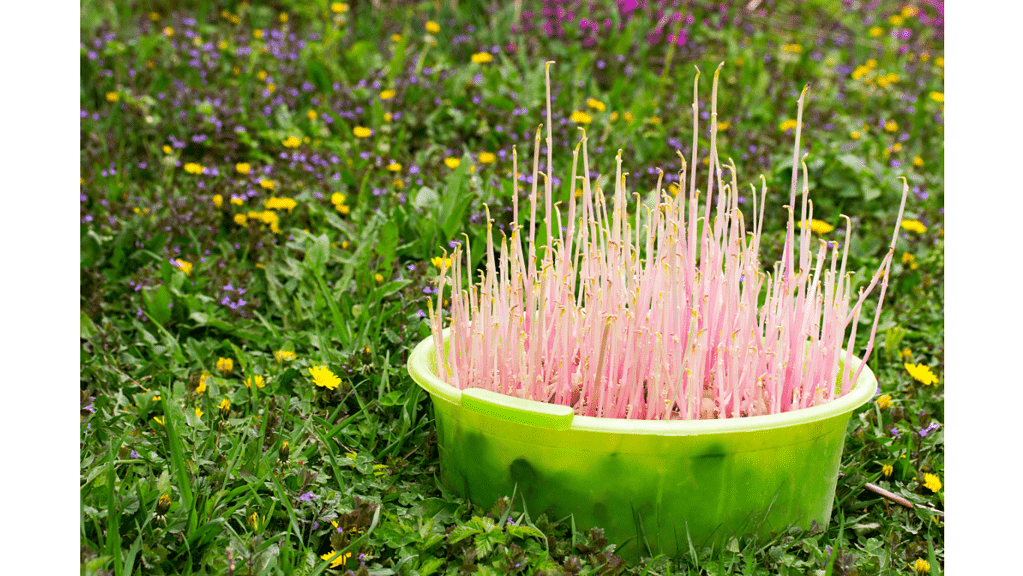

Most do not like to let anything go to waste. Once the potato is sprouting, you can still use it to start your own garden of potatoes. It is an excellent way to recycle, and you will not have to worry about buying potatoes if you grow them yourself.
They are easy to plant. It is best to grow them in a garden, not in a pot, because the plant is a never-ending vine. All you have to do is take the soil and dig a hole. Put the potato in the spot, cover it up, and add water.
The only thing to remember is not to let them grow wild. The vines will choke out other plants and attach themselves to anything and everything they come in contact with that is nearby.
It is the sprouts that will take root and grow from there.